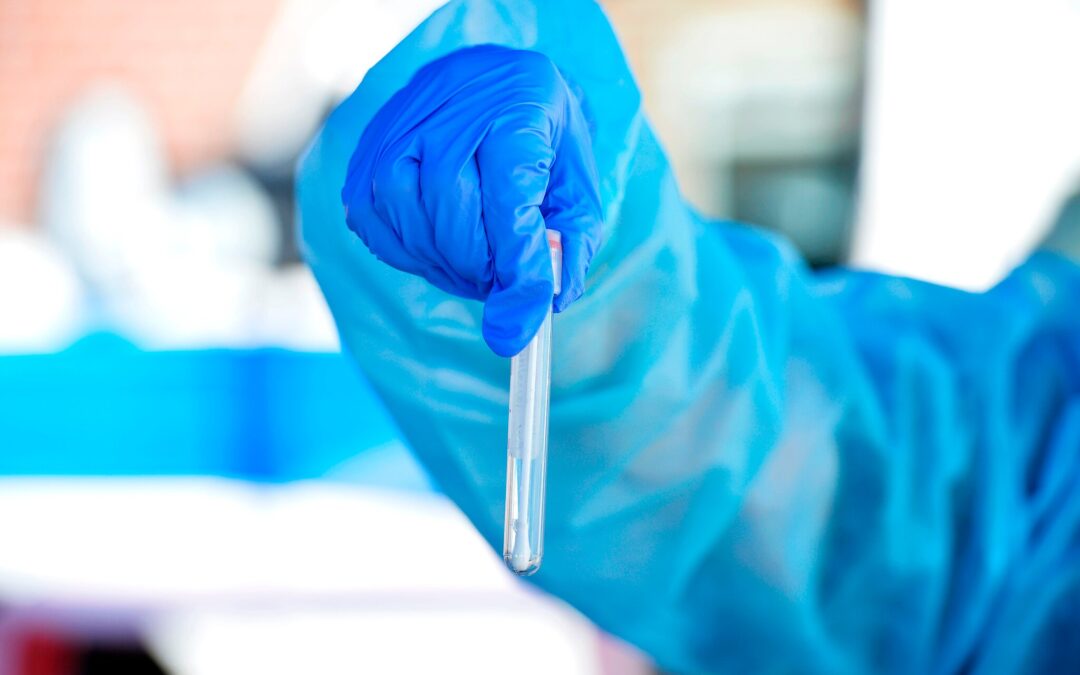
In the high-stakes world of coronavirus testing, false positives are widely considered to be benign in comparison with false negatives, which can deprive infected people of treatment and embolden them to mingle with others, hastening the spread of disease. But false positives, which incorrectly identify a healthy person as infected by the virus, can have serious consequences as well, especially in places where the virus is scarce. To read the full story.
Recent Posts
- NJACTS Community Engagement Core Available Services
- Unveiling the Biomechanical Forces that Drive Scarring.
- Scientists Discover Class of Crystals With Properties That May Prove Revolutionary.
- Will Banning Food Dyes Improve Our Health?
- Backed by Science and Evidence, New Jersey’s Actions Aim to Advance Maternal Health.
Categories
- Community (2,290)
- Covid (987)
- CTO Events (6)
- News (2,915)
- Pilots (21)